World History
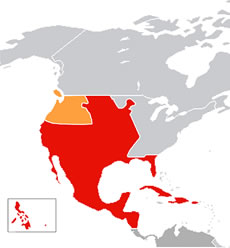 For 300 years (1521–1821), the Viceroyalty of New Spain, the richest and most important political jurisdiction in Spain’s American holdings, expanded from its original boundaries in central Mexico south and west to the Pacific Ocean; south and east to include the Yucatán Peninsula, Florida, the Caribbean, northern South America, and Central America to contemporary Panama (the latter in a jurisdictional subdivision called the Kingdom of Guatemala); and north to include significant portions of what later became the U.S. Southwest.
For 300 years (1521–1821), the Viceroyalty of New Spain, the richest and most important political jurisdiction in Spain’s American holdings, expanded from its original boundaries in central Mexico south and west to the Pacific Ocean; south and east to include the Yucatán Peninsula, Florida, the Caribbean, northern South America, and Central America to contemporary Panama (the latter in a jurisdictional subdivision called the Kingdom of Guatemala); and north to include significant portions of what later became the U.S. Southwest.
At the political, economic, and demographic center of this vast colony was the Basin of Mexico, at the heart of which lay Mexico City, built atop the ruins of the aztec capital of Tenochtitlán.
Consequences of Colonial Rule
Three hundred years of colonial rule bequeathed to New Spain an enduring legacy whose consequences remain amply apparent in Mexico and Central America today. Most fundamentally, the new colonial order created new social and racial hierarchies, with Spaniards dominant, Indians subordinate, and, as time passed, mestizos (“mixed-race†Spaniards and Indians) occupying a widening middle ground.
During the first century of colonial rule, the colony’s major social institutions can be identified as the following: the colonial state and its byzantine administrative apparatus; the Roman Catholic Church, both its “regular†and “secular†branches; encomienda; Indian communities; and the patriarchal family.
From around the mid-1600s, hacienda, generally accompanied by debt peonage, displaced encomienda as the principal institution governing land-labor relations between Spaniards and Indians, largely in consequence of steep population declines among Indians resulting from the ravages of epidemic diseases, which effectively rendered encomienda obsolete.
Secular Church's Power Grows
During the same period, the so-called secular church (the ecclesiastical hierarchy emanating from Rome, with the pope at its head) grew in power relative to the regular church (composed of quasi-independent missionary or “mendicant†orders such as the Franciscans, Dominicans, Augustinians, Jesuits, and others, each governed by specific reglas or rules).
This growing power of the secular church, densely entwined with the colonial state, was especially apparent in the most densely populated core regions, while the missionary orders remained strong in the colony’s peripheral zones, such as Yucatán, the northern deserts, and elsewhere.
The overall trend of the colonial period was for the regular church to initiate the process of conversion in peripheral areas, and, over time, as populations grew and the state extended its reach, to cede ecclesiastical authority to the encroaching secular church.
Far from a monolithic institution, the colonial church was wracked by division and conflict, both within and between its major branches. By the end of the colonial period, the Roman Catholic Church, both regular and secular, was not only one of the colony’s most important social institutions, but also far and away its largest landowner.
Contrary to a popularly held view, surviving Indian communities in New Spain and elsewhere retained various forms of collective (or “corporateâ€) landownership throughout the colonial period. This too became a crucial colonial legacy, especially evident in liberal efforts to privatize landownership in the decades after independence in 1821, efforts fiercely resisted by both the church and Indian communities.
Industry
The Basin of Mexico became and remained the colony’s breadbasket and major source of grain, meat, and other foodstuffs, as well as domestic industry such as obrajes, with expanding market relations especially important in the fertile and well-watered zones north and west of Mexico City.
In the 1540s, the discovery of large deposits of silver northwest of the Basin of Mexico, centered on the province of Zacatecas, provided the colonial state with a steady supply of silver bullion, fueling a price revolution in Iberia and the rest of Europe and transforming the regional colonial economies of Zacatecas, Guanajuato, and other mining regions.
By the mid-1600s, the sprawling colony sank into what one scholar dubbed “New Spain’s century of depression,†though the nature and extent of that “depression†remain the subject of scholarly debate. Compared to the thriving colonies of British North America and elsewhere, however, New Spain did experience a prolonged period of relative economic stagnation.
The imperial state’s efforts to redress its colonies’ relative economic decline, launched after the War of the Spanish Succession (1701–13), are known collectively as the Bourbon Reforms, named after the ruling dynasty that assumed power in Spain after the fall of the Habsburgs.
In a process similar to that unfolding elsewhere in the Americas, as time passed, the “creoles†(or criollos, i.e., Spaniards born in the Americas) became an increasingly important and powerful group, despite its relatively small size—a gradual shift that by the late 1700s led to a growing sense of American identity and the first stirrings for independence from Spain.
Indian and “mixed-race†rebellions and uprisings occurred throughout the colonial period, but most remained local and regional and focused on redress of specific grievances relating to colonial governance or perceived abuses by individual authorities.
Demographics
The demographic makeup of the colony changed markedly over time, from its initial overwhelming preponderance of Indians and tiny number of Spaniards, to steep Indian population decline, to increasing number of mestizos and others of “mixed race,†Africans, and a small but growing number of creoles.
New Spain’s population at the end of the colonial period is estimated at around 6 million—around 50 percent Indian, 30 to 40 percent “mixed race,†10 to 20 percent Spanish and creole, and less than 1 percent African.
In sum, 300 years of colonial rule left a profound and lasting legacy across New Spain, in every realm of society. Grappling with the nature of that legacy remains one of the most challenging and central tasks facing scholars of postconquest Mexico and Central America.
- Hacienda In Spanish America
Hacienda in Spanish America Hacienda (ah-see-END-ah) in Spanish America refers to the institution of private landownership, or a landed estate, owned by a hacendado (ah-sen-DA-doh). Hacienda emerged as the principal form of landownership, and one of the...
- Obrajes In Colonial Latin America
Obrajes in Colonial Latin AmericaObrajes (roughly, workshops) were key enterprises in the developing economies of Spain’s American colonies, principally as sites where wool, cotton, and other fibers were carded, spun, and woven into textiles. While...
- Reducciones (congregaciones) In Colonial Spanish America
Reducciones (Congregaciones) in Colonial Spanish America In response to steep demographic declines and a shared desire to exercise greater control over dwindling Indian populations, from the 1550s, Spanish colonial administrators and ecclesiastical authorities...
- Repartimiento In Spanish America
Repartimiento in Spanish America Rooted in the verb repartir (to distribute, to allot), repartimiento in Spanish America refers to two distinct institutional practices. One relates to encomienda during the first century of colonization, the second to...
- Silver In The Americas
The discovery of massive deposits of silver in New Spain and Peru from the mid-16th century set in motion a chain of events that reverberated across the globe. Large-scale silver production in Spanish America not only transformed local, regional, and...
World History
Viceroyalty of New Spain

At the political, economic, and demographic center of this vast colony was the Basin of Mexico, at the heart of which lay Mexico City, built atop the ruins of the aztec capital of Tenochtitlán.
Consequences of Colonial Rule
Three hundred years of colonial rule bequeathed to New Spain an enduring legacy whose consequences remain amply apparent in Mexico and Central America today. Most fundamentally, the new colonial order created new social and racial hierarchies, with Spaniards dominant, Indians subordinate, and, as time passed, mestizos (“mixed-race†Spaniards and Indians) occupying a widening middle ground.
During the first century of colonial rule, the colony’s major social institutions can be identified as the following: the colonial state and its byzantine administrative apparatus; the Roman Catholic Church, both its “regular†and “secular†branches; encomienda; Indian communities; and the patriarchal family.
  |   |
From around the mid-1600s, hacienda, generally accompanied by debt peonage, displaced encomienda as the principal institution governing land-labor relations between Spaniards and Indians, largely in consequence of steep population declines among Indians resulting from the ravages of epidemic diseases, which effectively rendered encomienda obsolete.
Secular Church's Power Grows
During the same period, the so-called secular church (the ecclesiastical hierarchy emanating from Rome, with the pope at its head) grew in power relative to the regular church (composed of quasi-independent missionary or “mendicant†orders such as the Franciscans, Dominicans, Augustinians, Jesuits, and others, each governed by specific reglas or rules).
This growing power of the secular church, densely entwined with the colonial state, was especially apparent in the most densely populated core regions, while the missionary orders remained strong in the colony’s peripheral zones, such as Yucatán, the northern deserts, and elsewhere.
The overall trend of the colonial period was for the regular church to initiate the process of conversion in peripheral areas, and, over time, as populations grew and the state extended its reach, to cede ecclesiastical authority to the encroaching secular church.
Far from a monolithic institution, the colonial church was wracked by division and conflict, both within and between its major branches. By the end of the colonial period, the Roman Catholic Church, both regular and secular, was not only one of the colony’s most important social institutions, but also far and away its largest landowner.
Contrary to a popularly held view, surviving Indian communities in New Spain and elsewhere retained various forms of collective (or “corporateâ€) landownership throughout the colonial period. This too became a crucial colonial legacy, especially evident in liberal efforts to privatize landownership in the decades after independence in 1821, efforts fiercely resisted by both the church and Indian communities.
Industry
The Basin of Mexico became and remained the colony’s breadbasket and major source of grain, meat, and other foodstuffs, as well as domestic industry such as obrajes, with expanding market relations especially important in the fertile and well-watered zones north and west of Mexico City.
In the 1540s, the discovery of large deposits of silver northwest of the Basin of Mexico, centered on the province of Zacatecas, provided the colonial state with a steady supply of silver bullion, fueling a price revolution in Iberia and the rest of Europe and transforming the regional colonial economies of Zacatecas, Guanajuato, and other mining regions.
By the mid-1600s, the sprawling colony sank into what one scholar dubbed “New Spain’s century of depression,†though the nature and extent of that “depression†remain the subject of scholarly debate. Compared to the thriving colonies of British North America and elsewhere, however, New Spain did experience a prolonged period of relative economic stagnation.
The imperial state’s efforts to redress its colonies’ relative economic decline, launched after the War of the Spanish Succession (1701–13), are known collectively as the Bourbon Reforms, named after the ruling dynasty that assumed power in Spain after the fall of the Habsburgs.
In a process similar to that unfolding elsewhere in the Americas, as time passed, the “creoles†(or criollos, i.e., Spaniards born in the Americas) became an increasingly important and powerful group, despite its relatively small size—a gradual shift that by the late 1700s led to a growing sense of American identity and the first stirrings for independence from Spain.
Indian and “mixed-race†rebellions and uprisings occurred throughout the colonial period, but most remained local and regional and focused on redress of specific grievances relating to colonial governance or perceived abuses by individual authorities.
Demographics
The demographic makeup of the colony changed markedly over time, from its initial overwhelming preponderance of Indians and tiny number of Spaniards, to steep Indian population decline, to increasing number of mestizos and others of “mixed race,†Africans, and a small but growing number of creoles.
New Spain’s population at the end of the colonial period is estimated at around 6 million—around 50 percent Indian, 30 to 40 percent “mixed race,†10 to 20 percent Spanish and creole, and less than 1 percent African.
In sum, 300 years of colonial rule left a profound and lasting legacy across New Spain, in every realm of society. Grappling with the nature of that legacy remains one of the most challenging and central tasks facing scholars of postconquest Mexico and Central America.
- Hacienda In Spanish America
Hacienda in Spanish America Hacienda (ah-see-END-ah) in Spanish America refers to the institution of private landownership, or a landed estate, owned by a hacendado (ah-sen-DA-doh). Hacienda emerged as the principal form of landownership, and one of the...
- Obrajes In Colonial Latin America
Obrajes in Colonial Latin AmericaObrajes (roughly, workshops) were key enterprises in the developing economies of Spain’s American colonies, principally as sites where wool, cotton, and other fibers were carded, spun, and woven into textiles. While...
- Reducciones (congregaciones) In Colonial Spanish America
Reducciones (Congregaciones) in Colonial Spanish America In response to steep demographic declines and a shared desire to exercise greater control over dwindling Indian populations, from the 1550s, Spanish colonial administrators and ecclesiastical authorities...
- Repartimiento In Spanish America
Repartimiento in Spanish America Rooted in the verb repartir (to distribute, to allot), repartimiento in Spanish America refers to two distinct institutional practices. One relates to encomienda during the first century of colonization, the second to...
- Silver In The Americas
The discovery of massive deposits of silver in New Spain and Peru from the mid-16th century set in motion a chain of events that reverberated across the globe. Large-scale silver production in Spanish America not only transformed local, regional, and...
